
The Road to Carbon Neutrality
--Low Carbon Emission Reduction Strategy of BBCA Biochemical
1. Environmental Footprint of Polylactic Acid
Polylactic acid (PLA) is considered to be the most potential material to replace the traditional plastic, can be used for injection molding, film, sheet, fiber and other plastic purposes. Under the goal of global low-carbon development and carbon neutrality in China, the low-carbon properties of polylactic acid have been recognized by the industry.
PLA has a wide range of raw materials. The first-generation PLA uses grain, cassava and other agricultural products as raw materials, while the second-generation PLA uses straw and other agricultural and agricultural product processing leftovers as raw materials. The existing PLA devices in the world and in China are mainly first-generation devices, and corn is the main raw material for PLA production in China. BBCA has planned to build the second-generation PLA pilot plant this year, and will use straw raw material to produce polylactic acid on a large scale in 2025. In the future, straw will gradually replace the dominant position of grain based PLA device.
In the evaluation of the environmental footprint of polylactic acid, calculated the carbon pool of corn. According to the energy utilization of domestic straw in the industrial chain (50% of straw is collected to make energy, and the energy conversion efficiency is 45%), each ton of polylactic acid is used to reduce 1.7-3.2 tons of carbon dioxide compared with the traditional materials PP, PE and PET.
2. Carbon Footprint of the PLA
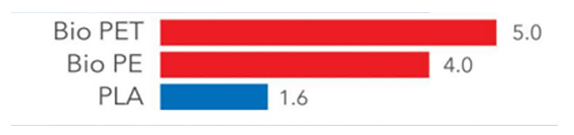
Compared with traditional petroleum-based polymers, PLA has reliable biosafety and biodegradable properties. Since PLA comes from biological bases, PLA has significant results in carbon reduction, with carbon emissions reduced by more than 68% than traditional petroleum-based plastics.
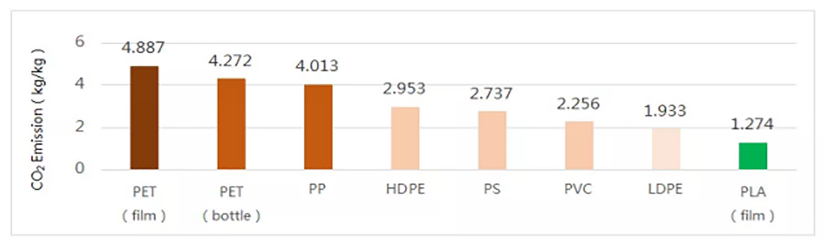
Use of carbohydrates in bioplastics (Plastic contains sugar in kilograms per kilogram).





 皖公网安备34032302020386号
皖公网安备34032302020386号